
Download Free Pdf Beginners Python Cheat sheet for all Programmers. When someone is trying out a set of exercises on a specific topic, or working on a project, cheatsheet can be really helpful. So programmer can fit so much information on just one sheet of paper, most fraudulent sheets are just a simple list of grammatical rules. A detailed Python cheat sheet with key data types, functions, and commands you should learn as a beginner. Free to download as PDF and PNG. View Python Cheat Sheet.docx from COMPUTER SOFTWARE E at Binus University. List = listi:j # returns list subset list-1 # returns last element list:-1 # returns all but the last element listi. Free Bonus: Python Cheat Sheet. Get a Python Cheat Sheet (PDF) and learn the basics of Python 3, like working with data types, dictionaries, lists, and Python functions.
Download Free Pdf Beginners Python Cheat sheet for all Programmers. When someone is trying out a set of exercises on a specific topic, or working on a project, cheatsheet can be really helpful. So programmer can fit so much information on just one sheet of paper, most fraudulent sheets are just a simple list of grammatical rules. The purpose of this set of deception sheets is to remind you of grammatical rules, but also to remind you of important concepts.
In this Pdf Book we have some important python cheat sheets topics
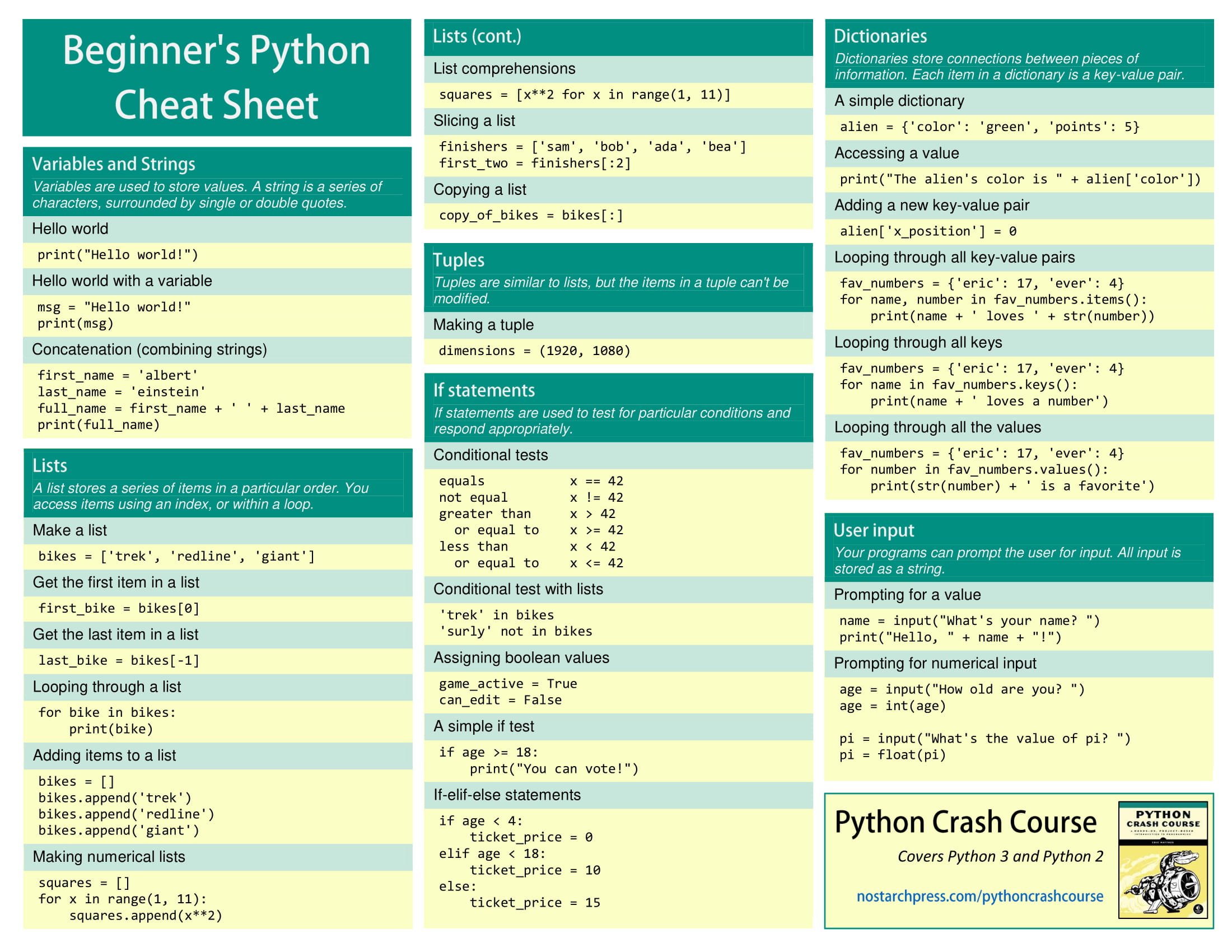
- Python Cheat Sheet
- Python Cheat Sheet – Lists
- Python Cheat Sheet – dictionaries
- Python Cheat Sheet – if statements and while loops
- Python Cheat Sheet – functions
- Python Cheat Sheet – classes
- Python Cheat Sheet – Files & Exceptions
- Python Cheat Sheet – Testing Code
- Python Cheat Sheet – Pygame
- Python Cheat Sheet – Matplotlib
- Python Cheat Sheet – Pygal
- Python Cheat Sheet – Django
Download Python CheatSheet
Download Python For Data Science CheatSheet
Download Python, Data Science, Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning CheatSheet
Basics
| Print a number | print(123) |
| Print a string | print('test') |
| Adding numbers | print(1+2) |
| Variable assignment | number = 123 |
| Print a variable | print(number) |
| Function call | x = min(1, 2) |
| Comment | # a comment |
Types
Free Python 3 Cheat Sheet
| Integer | 42 |
| String | 'a string' |
| List | [1, 2, 3] |
| Tuple | (1, 2, 3) |
| Boolean | True |
Useful functions
| Write to the screen | print('hi') |
| Calculate length | len('test') |
| Minimum of numbers | min(1, 2) |
| Maximum of numbers | max(1, 2) |
| Cast to integer | int('123') |
| Cast to string | str(123) |
| Cast to boolean | bool(1) |
| Range of numbers | range(5, 10) |
Other syntax
| Return a value | return 123 |
| Indexing | 'test'[0] |
| Slicing | 'test'[1:3] |
| Continue to next loop iteration | continue |
| Exit the loop | break |
| List append | numbers = numbers + [4] |
| List append (with method call) | numbers.append(4) |
| List item extraction | value = numbers[0] |
| List item assignment | numbers[0] = 123 |
Terminology
| syntax | the arrangement of letters and symbols in code |
| program | a series of instructions for the computer |
| print | write text to the screen |
| string | a sequence of letters surrounded by quotes |
| variable | a storage space for values |
| value | examples: a string, an integer, a boolean |
| assignment | using = to put a value into a variable |
| function | a machine you put values into and values come out |
| call (a function) | to run the code of the function |
| argument | the input to a function call |
| parameter | the input to a function definition |
| return value | the value that is sent out of a function |
| conditional | an instruction that's only run if a condition holds |
| loop | a way to repeatedly run instructions |
| list | a type of value that holds other values |
| tuple | like a list, but cannot be changed |
| indexing | extracting one element at a certain position |
| slicing | extracting some elements in a row |
| dictionary | a mapping from keys to values |
Reminders
- Strings and lists are indexed starting at 0, not 1
- Print and return are not the same concept
- The return keyword is only valid inside functions
- Strings must be surrounded by quotes
- You cannot put spaces in variable or function names
- You cannot add strings and integers without casting
- Consistent indentation matters
- Use a colon when writing conditionals, function definitions, and loops
- Descriptive variable names help you understand your code better
Conditionals
Lists
Defining functions
Loops
Dictionaries
Comparisons
| Equals |
| Not equals | != |
| Less than | < |
| Less than or equal | <= |
| Greater than | > |
Python Cheat Sheet Pdf
Useful methods
| String to lowercase | 'xx'.lower() |
| String to uppercase | 'xx'.upper() |
| Split string by spaces | 'a b c'.split(' ') |
| Remove whitespace around string | ' a string '.strip() |
| Combine strings into one string | ' '.join(['a', 'b']) |
| String starts with | 'xx'.startswith('x') |
| String ends with | 'xx'.endswith('x') |
| List count | [1, 2].count(2) |
| List remove | [1, 2].remove(2) |
| Dictionary keys | {1: 2}.keys() |
| Dictionary values | {1: 2}.values() |
| Dictionary key/value pairs | {1: 2}.items() |
Other neat bonus stuff
| Zip lists | zip([1, 2], ['one', 'two']) |
| Set | my_set = {1, 2, 3} |
| Set intersection | {1, 2} & {2, 3} |
| Set union | {1, 2} | {2, 3} |
| Index of list element | [1, 2, 3].index(2) |
| Sort a list | numbers.sort() |
| Reverse a list | numbers.reverse() |
| Sum of list | sum([1, 2, 3]) |
| Numbering of list elements | for i, item in enumerate(items): |
| Read a file line by line | for line in open('file.txt'): |
| Read file contents | contents = open('file.txt').read() |
| Random number between 1 and 10 | import random; x = random.randint(1, 10) |
| List comprehensions | [x+1 for x in numbers] |
| Check if any condition holds | any([True, False]) |
| Check if all conditions hold | all([True, False]) |
Missing something?
Let us know here.


